Union Find Model Algorithms
This particular module is focused on Union Find Model Algorithms.
A Union Find Model Algorithm is used to return if a node is connected to another through a path.
Example of a connected structure
Section titled “Example of a connected structure”- Set of N Objects
- Connection between two objects - UNION COMMAND
- Find if there’s a path connecting the two objects. (regardless of how many nodes are connected between) - CONNECTED, UNION FIND COMMAND

Applications of Union Find Models
Section titled “Applications of Union Find Models”- Pixels in digital media
- Networking
- Transistors in Chips
- Mathematical sets
- Variable Names in Fortran programs (????????What?????) <— Go look into this.
Modelling Connections and Definitions
Section titled “Modelling Connections and Definitions”Assume “is connected to” is an equivalence relation:
- Reflexive: p is connected to p. (Reflexive means referring to oneself using a pronoun e.g. Myself)
- Symmetric: if p is connected to q then q is connected to p.
- Transitive: if p is connected to q is connected to r, then p is connected to r.
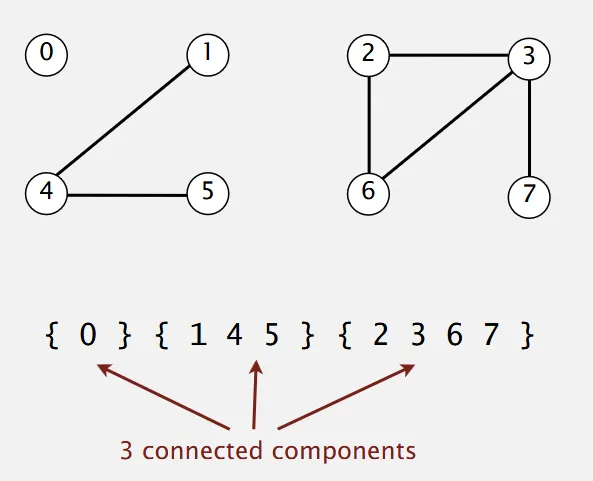
Connected Components: Connected components are a maximal set of objects that are mutually connected.
Operations
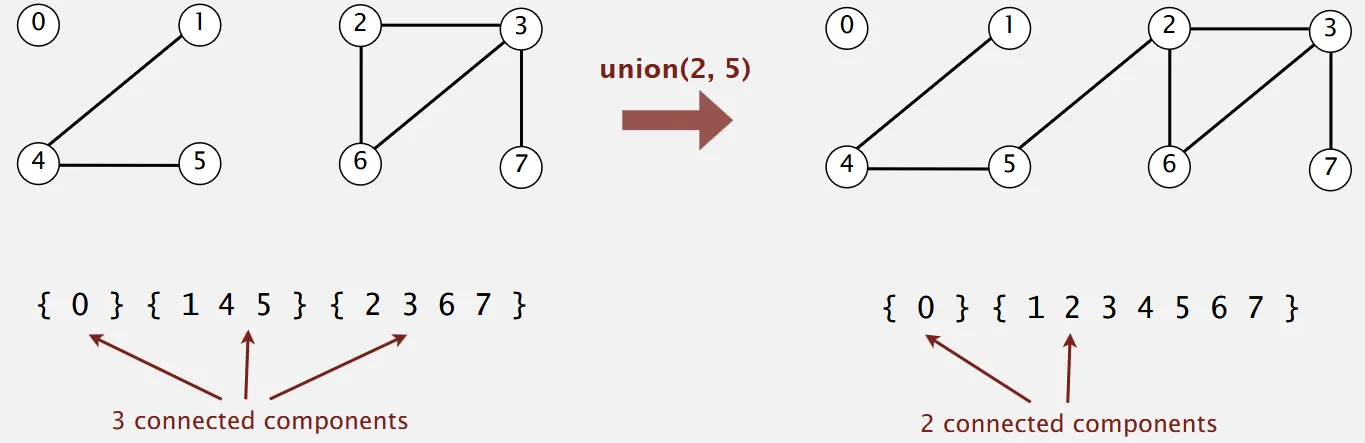
Section titled “Operations”Find Query: Check if two objects are in the same component.
Union Command: Replace components containing two objects with their union.
Union-Find Data Type (API)
Section titled “Union-Find Data Type (API)”In Java typically we would design a class called UF with two methods one for union and one for connected (Boolean return). Constructor takes number of objects as an argument.